Titanium Dioxide Reshaping the Field of the Cosmetic Industry - Nanografi
Titanium dioxide is an essential component widely used in the cosmetic industry. This inorganic substance is employed either as a white pigment or an inorganic UV filter in cosmetic products.
It can be found in sunscreens, foundations, powders, and various other cosmetic items. As a UV filter, titanium dioxide effectively protects the skin from the harmful effects of sunlight. Additionally, it imparts whiteness, opacity, and pigment to the products. The cosmetic industry harnesses the properties of titanium dioxide to enhance product stability and develop innovative formulations. Enhance your research and business with our Titanium Dioxide Nanografi products, which offer exceptional corrosion resistance and impressive thermal stability.
Introduction
The inorganic substance having a formula of TiO2 is known as titanium dioxide, titanium (IV) oxide, or titania. Pigment White 6 (PW6), titanium white, and CI 77891 are all alternate names for the substance when it is used as a pigment. Despite having black mineral formations, it is a white solid that is insoluble in water. Paint, sunscreen, and food coloring are just a few of the many products that may use as a pigment. It carries the E number E171 when used as a food coloring. Over 9 million tons were produced worldwide in 2014. The majority of all pigments are thought to include titanium dioxide, which has a market value of $13.2 billion for pigments made from the oxide.
With six oxide anions linked to it, titanium displays octahedral geometry in all three of its major dioxides. Three Ti centers are then linked to the oxides. Rutile, anatase, and brookite all have orthorhombic crystal structures, whereas rutile and anatase have tetragonal symmetry. In rutile, the oxide anions are grouped in deformed hexagonal close packing, but in anatase and brookite, they are near to cubic close packing and "double hexagonal close packing," respectively. The oxygen substructures are all modest distortions of close packing. For other metal dioxides and difluorides, including RuO2 and ZnF2, the rutile structure is common. Each Ti atom in molten titanium dioxide is coordinated to an average of five oxygen atoms in the local structure. Ilmenite is a mineral that is mostly used to make synthetic TiO2. As naturally occurring TiO2, rutile and anatase are very extensively distributed. For example, rutile is a "heavy mineral" in beach sand. Another ore is leucoxene, a fine-grained anatase created by ilmenite's spontaneous alteration. The rutile needle inclusions that are orientated give star sapphires and rubies their asterism.
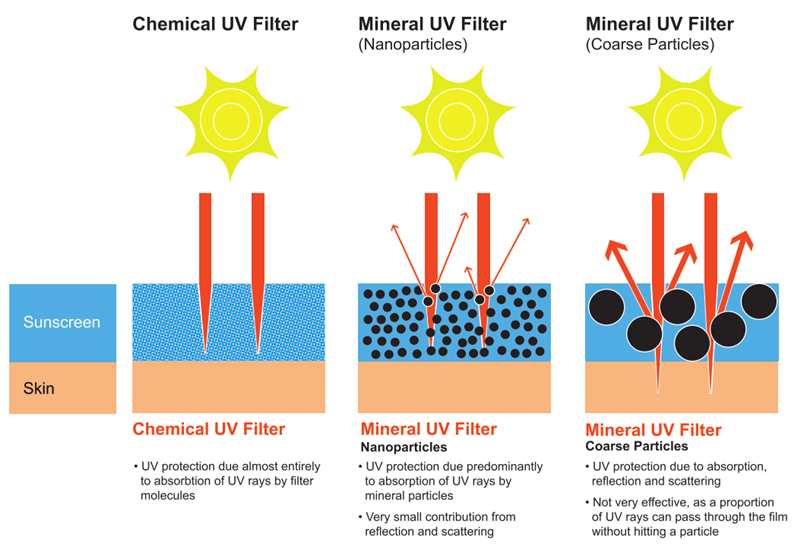
In order to protect against the known carcinogenic effects of UV radiation, TiO2 may be used in cosmetics either as a microcrystalline type of white pigment or as an inorganic ultraviolet (UV) filter, notably in sunscreens but also in some day creams, foundations, and lip balms. It is important to note that titanium dioxide with surface modifications is frequently used in the cosmetics industry to enhance physical and chemical stability, reduce powder dusting, improve pigment dispersions, and develop innovations that are not possible with conventional pigment. Treatments of every kind are available, including salts, esters, fluoropolymers, and different silicones; the hydrogen type and ethoxy type of silicone are the most often employed of these. Additionally, it should be highlighted that titanium dioxide is utilized in a wide range of items other than those related to cosmetics. It is a typical component of food, toothpaste, orthodontic materials, and paints. It is typically used as a food additive as an anti-caking or whitening agent, as well as to improve the color and gloss of food.TiO2 is also employed for its photocatalytic and biocidal properties. Because it absorbs nearly no incoming light in the visible range of the spectrum (380–700 nm), titanium dioxide is mostly used as a white pigment. Strongly dispersing incident light, titanium dioxide scatters it in three different ways: surface reflection, refraction, and diffraction in the crystal.
A Brief History of Titanium Dioxide
Since it was first used decades ago, titanium dioxide (also known as ci 77891) has been one of the most widely used chemicals in cosmetics. It is frequently employed as a pigment or brightener due to its natural occurrence, capacity for light refraction, and white hue. Titanium dioxide is a common ingredient in cosmetics, including sunscreen, treatments for sensitive skin, and ornamental cosmetics, in addition to soap and toothpaste. You'll find comprehensive details on the role of this element in this blog.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has authorized TiO2, a white powder, as a colorant in cosmetics and personal care items used on the skin, lips, nails, and other body parts. It aids in making product compositions more opaque and less transparent. Additionally, TiO2 absorbs, reflects, or scatters light (including UV rays from the sun) and shields sunscreen products from light's damaging effects. In order to shield the skin from the damaging effects of UV radiation from the sun, sunscreen products also include TiO2. Unprotected skin exposed to UV radiation runs the risk of developing skin cancer (mainly from UVA rays), sunburn (mostly from UVB rays), and early aging. Additionally, Australia, Canada, the European Union, and Japan have all accepted TiO2 as an active component in sunscreen.
A substance with several uses, titanium dioxide (TiO2) is frequently employed as a cosmetic or food additive. Its widespread use, particularly in nanoscale items, raises questions regarding its safety. This article reviews and organizes the most recent research on the safety of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) used as food additives or sunscreen compounds. Although some studies claim that humans cannot be harmed by cutaneous or oral exposure to TiO2 NPs, there is a substantial body of evidence showing that these particles are hazardous to animals. Researchers have not yet come to a consensus on this nanomaterial's safety as a whole. Additionally, there are no formal, defined standards from international authorities for the comprehensive characterization of TiO2 NPs in food and cosmetic goods. Recent developments in the use of "green-synthesized" TiO2 NPs are described, together with comparisons of the characteristics of "biogenic" and "traditional" nanoparticles.
Natural white mineral titanium dioxide, derived from ilmenite ore, is a frequent component in mineral-based cosmetics and sunscreens. According to scientists, titanium dioxide is inert, or chemically inactive. In contrast to chemical sunscreens that absorb UV radiation, titanium dioxide functions as a physical barrier when used as a sunscreen component. According to scientists, sunscreen shields skin by temporarily bonding with the top layer and preventing it from absorbing UV rays. Titanium dioxide is coated and broken down into tiny particles for use as a cosmetic component. Cosmetics are thickened and lubricated using this method.
Role of Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) in Cosmetic Products
Benefits of TiO2
Texture and Opacity:
In non-pigmented form, titanium dioxide (ci 77891) is used in cosmetics to enhance texture, provide a smooth and sheer appearance, and increase the opaqueness of a product. It helps in creating effective sunscreens as well as formulas that hide imperfections by providing uniform coverage.
Cosmetic Pigment:
Titanium dioxide in its pigmented form is a widely used cosmetic pigment. It imparts rich, intense sheen and color to various cosmetic products, including foundations, blushes, eyeshadows, and lipsticks. It offers versatility in creating different shades and hues.
Water Resistance and Oil Absorption:
Due to its water-resistant properties, titanium dioxide is often incorporated into long-lasting and water-resistant cosmetic products. It can help makeup stay in place and withstand moisture, making it suitable for activities such as swimming or exercising. Additionally, titanium dioxide has the ability to absorb excess skin oils, making it a desirable ingredient in oil control and mattifying cosmetics.
UV Protection: Titanium dioxide is utilized as a physical barrier in sunscreens to protect the skin from harmful UVA and UVB rays. It acts as a reflective shield, scattering and reflecting the UV radiation away from the skin. This helps to prevent sunburn, skin damage, premature aging, and the risk of skin cancer.
Non-irritating: Sunscreens and cosmetics containing titanium dioxide are often formulated to be gentle on sensitive skin. Titanium dioxide is a mineral ingredient that is less likely to cause irritation compared to synthetic materials found in some sunscreens. It can provide a soothing effect and is a suitable natural alternative for individuals with sensitive or inflamed skin.
Non-comedogenic: For individuals with acne-prone or easily congested skin, products containing titanium dioxide can be beneficial. Titanium dioxide is non-comedogenic, meaning it does not clog pores or contribute to the formation of acne. It is water-loving and easily rinses off the skin, making it suitable for those concerned about blocked pores, breakouts, and skin irritation.
Reduces the risk of early aging: Regularly using sunscreen with titanium dioxide, along with a minimum SPF of 30, can help protect the skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. This includes DNA damage, accelerated aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer. By safeguarding the skin, titanium dioxide can contribute to a fresher, cleaner appearance, reducing the appearance of lines, wrinkles, dark spots, and loss of elasticity.
Invisibility: If you prefer a sunscreen that doesn't leave a white cast on the skin, choosing one with titanium dioxide can be a good option. While some sunscreens may still require thorough blending, titanium dioxide can provide a more transparent finish compared to other UV filters. However, it's important to note that the transparency of sunscreen can depend on its specific formulation, so it's advisable to test different products to find the one that suits your needs.
Side effects of TiO2
In general, topical use of titanium dioxide has no negative side effects. It does not penetrate the skin and is not prone to trigger allergic responses. Normally, sunscreen does not emit any potentially harmful particles. There are a few factors to consider with titanium dioxide in cosmetics. Inhaling titanium dioxide-containing powders is not advised. Avoid using loose powders, blushes, eyeshadows, and sprays containing titanium dioxide. Stick to safe cream- or lotion-type formulations and choose products with a micronized formulation to give skin a smooth texture and prevent white casts, making such products more user-friendly and generally acceptable.
Uses of Titanium Dioxide in Cosmetics
Foundation and Concealers:
As a pigment, titanium dioxide is used in foundations and concealers to add color and coverage. It is also a common component in products for oily or mixed skin since it aids in the creation of a smooth, uniform texture and can aid in absorbing extra oil. Additionally, titanium dioxide contains built-in sun protection qualities that can aid in shielding the skin from UV deterioration.
Lipstick and Lip Gloss:
As a pigment to provide color, gloss, and opacity, titanium dioxide is frequently utilized in lip gloss and lipstick. The texture will be more equal and smoother, and the color will be less likely to bleed or feather. Additionally, since the lips are particularly vulnerable to sunburn and skin damage, titanium dioxide can aid in shielding them from UV rays.
Powder-based Products:
To achieve a matte look and add texture, titanium dioxide is frequently used in powder-based cosmetics like blushes and setting powders. It can aid in absorbing extra oil and establishing a uniform, smooth surface on the skin. Furthermore, titanium dioxide can assist to disperse light, which helps lessen the visibility of wrinkles and fine lines.
Eye Makeup:
As a pigment to provide color and opacity, titanium dioxide is often utilized in eye cosmetic products including eyeshadow, eyeliner, and mascara. It can aid in producing a smooth, uniform texture and aid in preventing smearing or fading of the color. Furthermore, titanium dioxide is frequently blended with other substances to provide long-lasting, waterproof solutions that are perfect for use on the delicate eye region.
Nail Polish:
Nail polish contains titanium dioxide as a whitener and opacifier. It can aid in producing a consistent, opaque hue and prevent it from turning too translucent or streaky. Additionally, titanium dioxide can aid in producing a uniform, smooth texture and can aid in preventing the chipping or peeling of the polish.
Hair Care Products:
In order to provide hold and structure to hair care products like styling gels and mousses, titanium dioxide is occasionally utilized. The hair can be kept from being too frizzy or unruly, and it can assist to produce a solid, long-lasting style. Due to the possibility of the chemical building up over time on the hair and scalp, titanium dioxide is used in hair care products less frequently than in other categories of cosmetics.
Texture Safety and Regulatory Considerations for Titanium Dioxide in Cosmetics
If titanium dioxide passes particular purity and particle size standards, it is thought to be a safe component for use in cosmetics. When used in accordance with industry standards, titanium dioxide is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) in cosmetics in the United States, where it is governed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Titanium dioxide nanoparticles, however, may have the potential to affect human health, according to certain research, thus it's crucial for manufacturers to thoroughly assess the safety of their goods before employing this element. Because of its capacity to offer color, opacity, and UV protection, titanium dioxide is frequently utilized in cosmetics and personal care products. It's crucial to remember that worries regarding the potential health effects of exposure to the substance have made the safety of titanium dioxide a hotly debated subject in recent years.
While titanium dioxide is often regarded as safe for use in cosmetics, some studies have revealed that the ingredient's nanoparticles may be able to enter the skin and harm cells, resulting in inflammation and other health issues. In certain research, it has also been hypothesized that being exposed to titanium dioxide nanoparticles may result in a higher risk of developing cancer.
Despite these issues, it is still thought that using titanium dioxide in cosmetics is safe as long as the chemical satisfies specific purity and particle size standards. When used in conformity with industry standards, titanium dioxide is generally regarded as safe (GRAS) in the United States, where the FDA oversees the use of the chemical in cosmetics. Before utilizing this chemical, producers should carefully assess the safety of their goods and take precautions to reduce any potential dangers related to contact with titanium dioxide nanoparticles.
Although TiO2 is safe for humans in small amounts, there have recently been a lot of worries regarding its usage in cosmetics. It is believed that this element may spread throughout the body and cross the skin barrier when it is in a nano form, potentially endangering human health. However, when applied to the skin at a concentration of up to 25%, titanium dioxide nanoparticles aren't harmful, according to the Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety. Scientists have disproved the claims that dangerous compounds containing TiO2 in composition when applied to the skin are carcinogenic, mutagenic, or poisonous to the developing fetus.
The Future of Titanium Dioxide in Cosmetics and Emerging Trends
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is anticipated to keep playing a prominent role in the cosmetics sector in the future. In many cosmetic products, such as foundations, powders, sunscreens, and lipsticks, TiO2 is a versatile component that is frequently employed as a white pigment. It gives these products opacity, UV defense, and a brightening effect. The safety of TiO2 nanoparticles and their possible negative impacts on health when breathed or swallowed, however, have come under increasing scrutiny. As a result, the usage of TiO2 in cosmetic formulations is receiving increased attention from regulatory organizations and consumers. The industry is now looking at alternative ingredients and technologies as a result of this.
The following new developments in the use of titanium dioxide in cosmetics include:
- A shift toward non-nano formulations: The demand for non-nano formulations in cosmetics is rising as a result of the worries around TiO2 nanoparticles. The bigger particle sizes of non-nano TiO2 particles lower the danger of skin absorption and provide better safety profiles.
- The utilization of alternative UV filters: Due to its capacity to reflect and scatter UV light, titanium dioxide is frequently utilized as a physical sunscreen ingredient. Alternative UV filters that offer adequate protection without the possible side effects of TiO2 nanoparticles, however, are gaining popularity. Alternative ingredients including zinc oxide, Tinosorb, and Mexoryl SX are becoming more and more well-liked.
- Goods and hybrid formulations: They are becoming less distinct as customers look for multifunctional goods that offer both cosmetic and skincare advantages. These formulations frequently include titanium dioxide because of its aesthetic advantages while also including other skincare-beneficial components including antioxidants, moisturizers, and anti-aging agents.
- Transparency and labeling: There is a rising emphasis on transparency and correct labeling as a result of the increased knowledge of and concerns about the use of TiO2 in cosmetics. Manufacturers must conform to regulatory agencies' labeling guidelines and offer precise information about the TiO2 particle size utilized in their goods.
- Research and development: Attempts to produce UV filters and other white pigments that might replace or reduce the requirement for titanium dioxide in cosmetics are still being made. These projects aim to provide safer and greener alternatives without losing product performance.
It's important to remember that these trends are influenced by continuing studies, governmental changes, and consumer preferences. The future of titanium dioxide in cosmetics must be decided by scientists, regulators, and industry stakeholders in order to ensure product safety and meet consumer demand.
Conclusion
Titanium dioxide is well-known for its capacity to absorb light in the UVB region (280-315 nm), which is synonymous with sun protection. It is commonly combined with a UVA absorber (315–400 nm), such as zinc oxide, to provide the wearer with comprehensive UV protection. However, only around 8% of titanium dioxide is used globally for sun protection. Around 80% of the material's overall use is made up of paints, varnishes, paper, and plastics, which include the majority of the material. The high refractive index of titanium dioxide, or its capacity to bend or deflect light when it interacts with a surface or medium, is what gives it its usefulness. Due to its high level of visible light reflection, the material appears bright or "brilliant white" to the unaided eye. It is one of the most well-known and economically significant inorganic pigments as a result, and it is frequently used to give products like paper, paint, medicines, food, and cosmetics an opaque or white appearance. With Nanografi's Titanium Dioxide products, businesses can produce high-quality products and establish a more reliable position in the cosmetics industry.
References
Musial, J., Krakowiak, R., Mlynarczyk, D. T., Goslinski, T., & Stanisz, B. J. (2020). Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Food and Personal Care Products-What Do We Know about Their Safety? Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland), 10(6), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.3390/NANO10061110Racovita, A. D. (2022). Titanium Dioxide: Structure, Impact, and Toxicity. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, Vol. 19, Page 5681, 19(9), 5681. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJERPH19095681
Titanium Dioxide - Cosmetics Info. (n.d.). Retrieved March 20, 2024, from https://www.cosmeticsinfo.org/ingredient/titanium-dioxide/
Titanium dioxide - Wikipedia. (n.d.). Retrieved March 20, 2024, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Titanium_dioxide
Titanium Dioxide for Skin: Benefits and the Best Products. (n.d.). Retrieved March 20, 2024, from https://www.byrdie.com/titanium-dioxide-for-skin-5225320
Titanium dioxide in the cosmetics industry - The Health Science Journal. (n.d.). Retrieved March 20, 2024, from https://www.thehealthsciencejournal.com/titanium-dioxide-in-the-cosmetics-industry/
Why Zinc Oxide is The Best Choice For Natural Sunscreens – Suntribe ® - Online Store. (n.d.). Retrieved March 20, 2024, from https://goodtopssm.life/product_details/7854050.html
Recent Posts
-
Advanced Materials for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Protection Against Laser
Consider a UAV on a critical mission, rendered inoperative by a sudden laser attack. With the increa …26th Jul 2024 -
Simulation and Modeling of Material Properties
Our world is composed of a dazzling array of materials, each with its own unique properties that dic …19th Jul 2024 -
Advanced Coatings for Superior Corrosion and Wear Resistance
Corrosion and wear pose significant challenges across various industries, leading to substantial eco …12th Jul 2024






