Shape Memory Alloys
Shape memory alloys (SMAs) are combined metallic materials that can “remember” their original form after mechanical or thermal stimuli. The shape memory behavior of SMAs is caused by the shape memory effect (SME) and pseudoelasticity. The shape memory effect of SMAs stems from the transformations between austenite and martensite structures. The shape memory effect shows two different characteristics: one-way shape memory effect (OWSME) and two-way shape memory effect (TWSME). While the one-way shape memory effect is an intrinsic behavior of SMAs, the two-way shape memory effect is a trained behavior. The most important shape memory alloys are NiTi based, Cu-based, Fe based, and NiAl based SMAs. An average of 6-8% strain is observed for SMAs. The transformation temperature of SMAs can vary between 100-1150°C. Application areas of SMAs are;
- Automotive applications (tumble flaps, protection systems, actuators…)
- Aerospace applications (vibration dampers, actuators, pathfinders…)
- Robotic applications (actuators and sensors)
- Biomedical applications (Implants, braces, medical equipment…)
- Product
- Qty in Cart
- Quantity
- Price
- Subtotal
-

Nitinol Shape Memory Alloy Wire, Diameter: 1,5 mm, AF: 35-40°C
€60.001 meter / 60 € 5 meters / 210 € 10 meters / 620 € Please...NG01SMA003€60.00 -

Nitinol Shape Memory Alloy Wire, Diameter: 0,5 mm, AF: -10 - -15°C
€50.001 meter/ 50 € 5 meters/ 185 € 10 meters/ 250 ...NG01SMA001€50.00 -

Nitinol Shape Memory Alloy Sheet, Thickness: 0,5 mm, AF: 35-40°C
€6.851cm x 1cm/ 6,85 € 2 cm x 2cm/ 16 € 5 cm x 5cm/ ...NG02SMA003€6.85 -
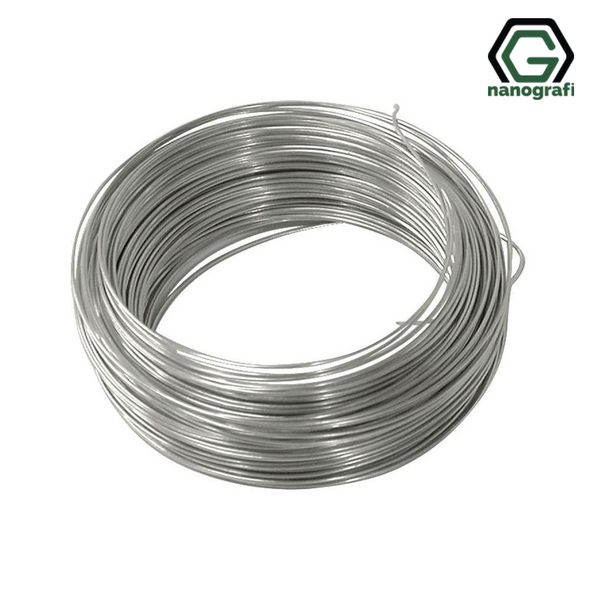

Nitinol Shape Memory Alloy Wire, Diameter: 1 mm, AF: 15-20°C
€45.001 meter / 45 € 5 meters / 180 € 10 meters / 250 € Please...NG01SMA002€45.00 -
Nitinol Shape Memory Alloy Sheet, Thickness: 0,5 mm, AF: 80-85°C
€6.801cm x 1cm/ 6,80 € 2 cm x 2cm/ 16 € 5 cm x 5cm/ ...NG02SMA005€6.80 -

Nitinol Shape Memory Alloy Wire, Diameter: 1 mm, AF: 45-50°C
€45.001 meter / 45 € 5 meters / 180 € 10 meters / 246 € Please...NG01SMA004€45.00 -

Nitinol Shape Memory Alloy Wire, Diameter: 2 mm, AF: 80-85°C
€40.001 meter / 40 € 5 meters / 160 € 10 meters / 220 € Please...NG01SMA005€40.00 -

Nitinol Shape Memory Alloy Sheet, Thickness: 2 mm, AF: -10 - -15°C
€4.501cm x 1cm/ 4,50 € 2 cm x 2cm/ 6,75 € 5 cm x 5cm/ ...NG02SMA001€4.50 -

Nitinol Shape Memory Alloy Sheet, Thickness: 1 mm, AF: 50-55°C
€6.201cm x 1cm/ 6,20 € 2 cm x 2cm/ 12,45 € 5 cm x 5cm/ ...NG02SMA004€6.20
