Rare Earth Elements in Cancer Diagnosis & Treatment
The Rare Earth elements are very special and are used in most modern technologies. The Rare Earth elements include as many as 17 chemical elements, which in recent years have become very precious and refined. In many productions (magnets, catalysts, displays) the Rare Earth elements are indispensable. The Rare Earth elements are these: dysprosium (Dy), cerium (Ce), erbium (Er), gadolinium (Gd), europium (Eu), holmium (Ho), Lutetium (Lu), lanthanum (La), neodymium (Nd) , promethium (Pm), praseodymium (Pr), samarium (Sm), terbium (Tb), scandium (Sc), thulium (Tm), yttrium (Y) and ytterbium (Yb). Among the rare earth elements, there are 15 lanthanides plus scandium and yttrium. Cerium, lanthanum, and neodymium are the rare earth elements that are mostly produced. The rare earth elements have many medical applications. In this article, we will review the applications of a few rare earth elements in Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment.
But, let’s first have a look at the occurrence of rare earth elements.
Disclaimer: The content of this post or any other linked material is intended for informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice.
Occurrence of Rare Earth Elements
The world production of rare earth oxides exceeds 125 thousand tons, and China is the leader with about 85% of Rare Earth elements production. Canada, Greenland, and Australia should offer significant sources for the future, but Japan is the leader of the future with a huge recently discovered field.
In 1992, China realized that the future of their country lies in the rare earth. Although the metals are not nearly as rare as initially suspected. Nevertheless, worldwide deposits are distributed over long distances. And even within these deposits, the degradable amounts are relatively small compared to other precious metals or minerals. The degradation of rare earth elements is therefore often complicated.
Therefore, the largest deposits so far are actually found in China (about 36 million tons) and in the US (about 13 million tons). Other deposits are located in Brazil, India, and Malaysia. Another large mining area could arise in Greenland, which is believed to be up to 2.6 million tons.
Rare Earths in the Periodic Table of Elements.
Use of Rare Earth Elements in Cancer Diagnosis & Treatment
The use of some of the rare earth elements in Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment is discussed below in detail:
1. Yttrium for Liver Cancer Treatment
In recent years, we have witnessed a very important role of Yttrium in Cancer Treatment. Yttrium-90 microsphere therapy at the Clinica Universidad de Navarra achieved local control of liver cancer in more than 80% of cases. The University has been applying a Ytrio-90 microsphere treatment for 16 years, which managed to control liver cancer locally in more than 80% of cases. The therapy has already been applied to more than 400 patients.
The technique consists of injecting spheres of a very few microns in size, loaded with the radioactive isotope Ytrio-90, into the hepatic artery, from where they are directed preferentially to the tumor lesion. There they are housed and emit radiation, damaging the tumor cells. In primary liver tumors, also called hepatocarcinomas, the results show that the treatment is very effective in preventing the treated lesions from growing.
The treatment with Yttrium microspheres is a complex and multidisciplinary procedure that requires the close collaboration of the departments of Nuclear Medicine, Conventional and Interventional Radiology, Hepatology, Oncology, and its HepatoBilioPancreatic Area.
The treatment of liver tumors by radioembolization has the advantage of not being an exclusive procedure. It can be administered in combination with chemotherapy, in those tumors that are sensitive to this treatment. In addition, it is well-tolerated, does not require large hospital admissions, (usually patients remain admitted a single day, they may not even need admission), and have a low risk of complications.
Yttrium-90 microsphere therapy is no longer an experimental treatment, but a reality that contributes to improving the survival of patients undergoing this treatment.
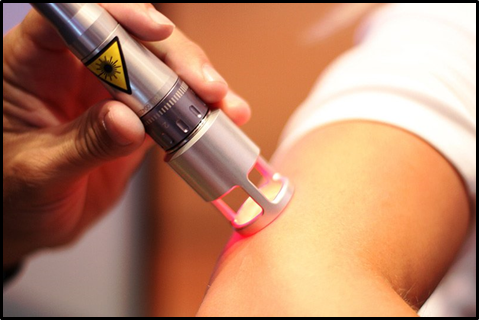
2. Neodymium for the Treatment of Skin Cancer
Neodymium is another rare earth metal with a huge potential for cancer treatment. Neodymium laser therapy is of great importance for skin cancer. Neodymium emits at a wavelength of 1.32 microns in the near-infrared. It produces protein coagulation in a sphere around its emission point. It seals blood vessels through thermal action.
The dermatological Neodymium laser is an effective weapon in the therapy of skin cancer, which over time has improved its effectiveness. LASER, an acronym whose meaning is light amplified by stimulated emission of radiation, in its simplest form is a light source, where radiant energy is in the form of photons and waves capable of producing special biological effects. As a general concept, the term laser corresponds to devices that generate or amplify coherent radiation of light in the infrared, visible and ultraviolet regions of the spectrum.
The laser light is generated by stimulating the passage of low energy orbitals to high energy orbitals of the electrons of the Neodymiumelement, which is located in the laser chamber, once the element has been excited and affects the photon, the electron returns to its low energy orbital emitting two photons with the same momentum and at the same speed.
All medical lasers have four components: an optical cavity or resonance tube, which surrounds a laser medium, an energy source, and a laser light management system. The laser medium can be a solid, liquid or gas element and is what gives the system its name. The excitation process occurs when an external source of energy, called a "pump" sends energy to the system. This is usually electricity, radiofrequency, light or a chemical reaction. In this way the inversion of the medium is achieved, that is, to make the electrons of the medium pass from their low energy levels to the high energy levels.
Some of the excited electrons release energy spontaneously in the form of two photons when they return to their low energy state. This phenomenon is amplified by the optical cavity surrounding the medium, which are mirrors that reflect the emitted photons. These, when affecting the other excited atoms, produce the return of the excited elements at lower energy levels and the emission of more photons by the medium, the resulting energy is emitted by a small perforation in a mirror and is sent by the administration system of the laser, either through hollow rigid tubes, which contain mirrors on the elbows or along optical fibers or flexible and hollow fibers.
3. Cerium Oxide as an Antioxidant
The creation of innovative cerium oxide nanoparticles also serves in the treatment of cancer patients. One more application that joins the long list of uses of this rare earth metal.
Although the name cerium oxide does not call your attention too much, the truth is that thousands of people use this chemical compound daily. Recent research even relates to this oxide with a possible application in the treatment of cancer patients. Its formula CeO2 gives us a clue as to its origin, since it derives from cerium, one of the fifteen chemical elements known as lanthanides, and that owes its name to the asteroid Ceres.
Beyond the etymological origin of its name, cerium oxide retains some really interesting chemical properties. A small amount, around 2%, protects the crystals from possible damage caused by radiation, in addition to serving as a UV filter.
Research has been conducted at Rice University on the use of Cerium Oxide for Cancer treatment. In particular, the research focused on the creation of small biocompatible spheres of this chemical compound, through the use of oleic acid. These could be used in patients affected by different types of cancer. The creation of these authentic nanoparticles presents really important future applications in medicine.
In addition, the size of these nanoparticles is ideal, so that in the future they could be administered to patients who need it. Its antioxidant effect allows them to "absorb" reactive oxygen particles, so that it "breaks" in some way these free radicals, causing them to not cause any damage. The use of these nanoparticles could be interesting in cancer patients treated with radiotherapy. In this way, cerium oxide spheres would be used as radioprotectors, since those that currently exist have to be given in very high doses, so they cause dangerous side effects.
Perhaps this is the first time that nanoparticles of this type, and in particular cerium oxide, have been devised with such an important medical application. This advancement is being used to treat cancer patients in clinical practice. It is clear that the combination of nanotechnology and medicine presents a successful future ahead.
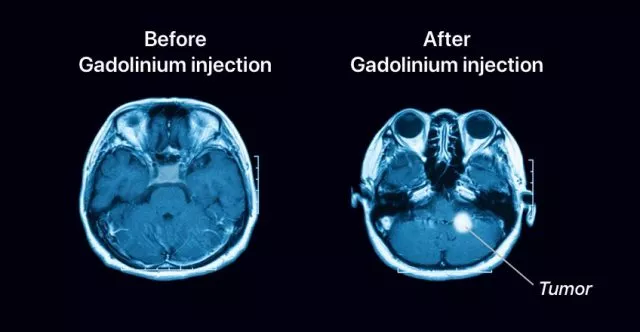
4. Gadolinium Nanoparticles as an MRI contrast
Gadolinium is another element that belongs to the group called 'rare earth', those new materials that, due to their electromagnetic properties, help technology so much. Gadolinium is a key rare earth metal for detecting tumors in the brain. Gadolinium, in particular, favors doctors who fight against brain cancer, who use it in MRI as a contrast material. Gadolinium helps to locate small tumors, to which gadolinium stains its own color: silver-white. Gadolinium which in the injected dose (0.1-0.2 mmol/kg), decreases the T1 of those structures in which it accumulates causing its increase in signal in the sequences weighted in T1.
Image Source: Gadolinium - drugwatch.com
5. Samarium for the treatment of Bone Metastases
Another rare earth metal that plays a key role in cancer treatment is Samarium. Samarium-153-Lexidronam (EDTMP) is used in the treatment of bone metastases. Bone metastases are a frequent complication in neoplastic patients, in this sense, the bone tissue is in the third place of systems with metastases after the lung and liver. Between 60-84% of neoplastic patients develop bone metastases and their incidence varies depending on the type of primary tumor: 73% in breast cancer, 68% in patients with prostate cancer, 42% in the Thyroid cancer, 36% in lung cancer and 35% in renal, morbidity being greater in the two initial groups, as a consequence of its slow evolution.
Thus, with the digital boom and new medical technologies, today, in the global economy, rare earth elements are considered strategic metals. There are 17 rare earth metals: scandium, yttrium, and fifteen lanthanides. These mineral materials with exceptional properties are used in different medical applications. China currently produces much of the world production of rare earth elements, especially in Mongolia and Sichuan. Some rare earth elements are of huge importance for Cancer diagnosis and treatment, as described above.
Recent Posts
-
Turning Noise into Power: Energy Harvesting with Piezoelectric Nanogenerators
Ambient acoustic energy, once an untapped resource, is now being converted into sustainable electric …5th Mar 2025 -
Holey Super Graphene in Li-ion Batteries: Next Generation of Energy Storage
Holey Super Graphene (hG), also referred to as “holey graphene,” is redefining li-ion ba …7th Feb 2025 -
Future Communication with 5G Technology and Advanced Materials
5G technology opens the doors to a new era in communication with faster connection speeds, low laten …6th Feb 2025