Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
What are Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWCNTs, SWNTs)? - Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes are one-atom-thick sheets of carbon atoms in a honeycomb lattice that accumulate to shape long hollow tubes with walls. Single-walled CNTs own remarkable electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties and are regarded as a standout amongst the most encouraging nanomaterials for applications and essential research. The noteworthy electrical properties of SWCNTs originate from the strange electronic structure of the two-dimensional material, graphene, from which they are built. Individual Single-Walled CNTs have current conveying limits of 109 amp/cm2, higher than those of copper or gold, and semiconducting species show higher electron versatility than silicon. Their electrical conductivity can indicate metallic or semiconducting behavior with varying band gaps, depending upon the orientation of the lattice. Therewithal this capacity to show both metallic and semiconducting electronic structures, Single-Walled CNTs offer extraordinary charge bearer mobilities. Remarkable mechanical properties of Single-Walled CNTs are obtained from a blend of strictness, endurance, and tenacity. Individual Single-Walled CNTs are essentially stronger than steel. Computed esteems for rigid qualities of single-walled carbon nanotubes are ~ 100 times more prominent than steel at 1/sixteenth the weight. Single-walled CNTs have also been utilized for thermal protection as thermal interface materials. Along the length of the tube, thermal conductivity can be up to 9 times higher than materials such as copper.
Applications - In favor of their unique electronic and mechanical properties, Single-Walled CNTs can be used in countless applications such as field-emission displays, nanocomposite materials, nanosensors and logic elements.
- Product
- Qty in Cart
- Quantity
- Price
- Subtotal
-
Large Surface Area Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Purity: > 95%, SSA: 400 m2/g
€175.001 gram/175 € 5 grams/679 € Please contact us for quotes on larger quantities !!! Large Surface Area Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes Purity: > 95%,...NG01SW0601€175.00 -
Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Purity: > 96%, Dia: 1.0 nm
€215.001 gram/215 € 5 grams/710 € 25 grams/2730 € Please...NG01SW0501€215.00 -
POPULAR
Short Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Purity: > 65%, SSA: 400 m2/g
€70.001 gram/70 € 5 grams/195 € 25 grams/820 € Please contact us for quotes on larger...NG01SW0401€70.00 -
Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Purity: > 92%, OD: 1-2 nm
€100.001 gram/100 € 5 grams/355 € 25 grams/1345 € ...NG01SW0301€100.00 -
(-COOH) Functionalized Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Purity: > 92%, SSA: 370 m2/g
€117.001 gram/117 € 5 grams/449 € 25 grams/1793 € Please contact us for quotes on...NG01SW0103€117.00 -
(-COOH) Functionalized Short Length Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Purity: > 92%
€210.001 gram/210 € 5 grams/840 € 25 grams/3730 € ...NG01SW0203€210.00 -
(-COOH) Functionalized Short Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Purity: > 65%
€99.001 gram/99 € 5 grams/270 € 25 grams/1055 € Please contact us for quotes on larger...NG01SW0403€99.00 -
(-COOH) Functionalized Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Purity: > 65%
€65.001 gram/65 € 5 grams/179 € 25 grams/750 € Please contact us for...NG01SW0303€65.00 -
(-OH) Functionalized Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Purity: > 65%
€60.001 gram/60 € 5 grams/169 € 25 grams/708 € ...NG01SW0302€60.00 -
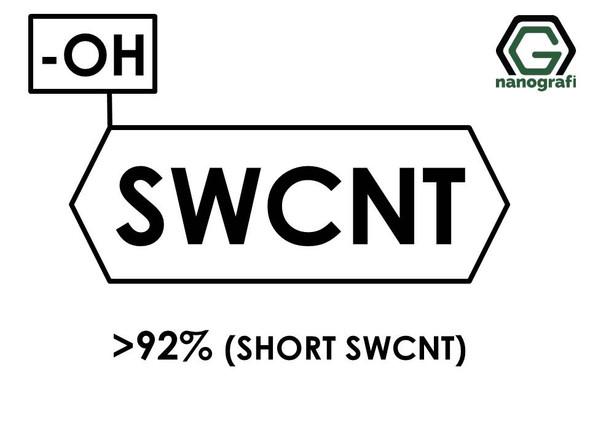
(-OH) Functionalized Short Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Purity: >92%
€188.001 gram/188 € 5 grams/752 € 25 grams/2730 € Please contact us for quotes...NG01SW0202€188.00 -
(-OH) Functionalized Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Purity: > 92%, SSA: 370 m2/g, Dia: 1.0 nm
€117.001 gram/117 € 5 grams/449 € 25 grams/1793 € Please contact us for quotes on larger...NG01SW0102€117.00 -
Short Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Purity: > 92%
€170.001 gram/170 € 5 grams/615 € 25 grams/2630 € ...NG01SW0201€170.00